If you’re an avid gardener, you’ve likely encountered these tiny adversaries – June Bugs and Japanese Beetles. While they might appear similar at first glance, these garden insects have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Understanding the differences between these June bug and japanese beetle is key to protecting your precious plants and ensuring a blooming garden all season long.
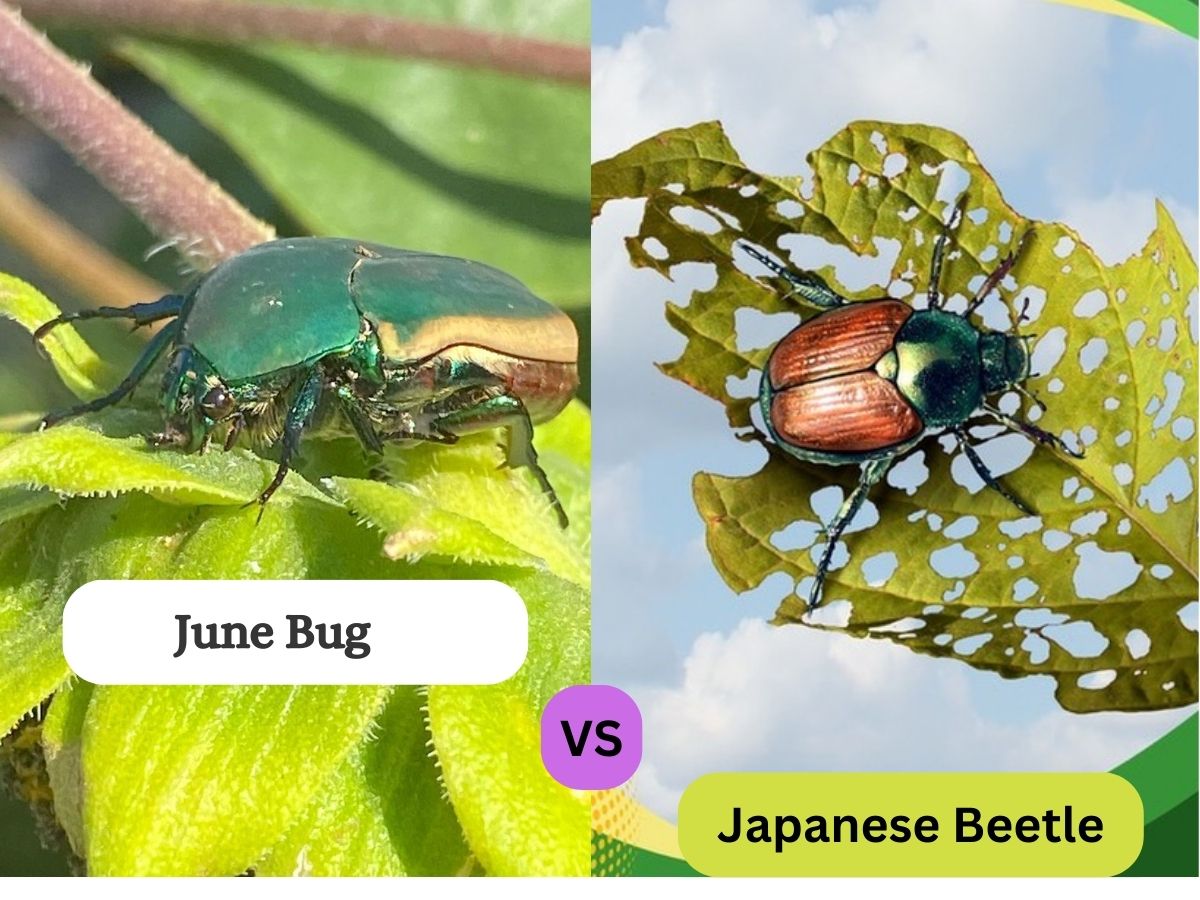
June Bugs, also known as June Beetles, are fascinating creatures with their reddish-brown hue and fan-like antennae. They make their presence known during warm summer evenings, often found buzzing around porch lights with their unmistakable drone.
On the other hand, the Japanese Beetle, a beautiful yet voracious invader, sports a metallic green body and coppery-brown wings adorned with tiny white tufts of hair. Introduced to North America, they have quickly made a name for themselves as notorious garden pests, leaving a trail of destruction in their wake.
In this article, we’ll delve into the distinct physical characteristics, life cycles, behaviors, and geographic distributions of June Bugs and Japanese Beetles. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge you need to confidently identify and manage these garden invaders, protecting your oasis of greenery from their munching appetites. So, let’s jump right into the enthralling battle of the beetles.
June Bug: The Backyard Buzzers
Meet the delightful June Bug, the buzzing charmers of our gardens;
Physical Characteristics:
June Bugs, also known as June Beetles, are fascinating creatures with their own unique charm. These critters boast a size of around 1 inch, making them larger than some of their beetle buddies. Sporting an oval-shaped body, they exude a warm reddish-brown hue, which can sometimes shimmer in the sunlight, adding to their allure.
Now, here’s the secret to spotting a June Bug amidst the crowd of insects: check out their antennae. Unlike other beetles, June Bugs flaunt fan-like antennae at the top, resembling a cool pair of antennas worthy of admiration.

Life Cycle and Behavior:
As creatures of nature, June Bugs follow a remarkable life cycle that’s worth unraveling.
- Egg-laying habits and locations: Female June Bugs lay their eggs in the soil during the warmer months, usually in early summer. These eggs hatch into tiny, hungry grubs that embark on their underground journey.
- Larval stages and their impact on lawns and gardens: The C-shaped grubs feed on plant roots and organic matter beneath the soil. While their presence might not be noticeable at first, their insatiable appetite can lead to brown patches and weakened lawns if their population becomes substantial.
- Adult behaviors and feeding patterns: Once their larval phase is complete, June Bugs emerge as adults, ready to take the garden stage. You’ll often spot them during warm evenings, attracted to light sources like porch lights. As nighttime flyers, they might accidentally find their way indoors, causing momentary chaos. When it comes to diet, June Bugs prefer munching on leaves, but don’t worry, they are not as destructive as their Japanese Beetle counterparts.
June Bugs are quite the social butterflies; you can find them mingling in various parts of the world. They are commonly spotted across North America, Europe, and Asia, creating a global garden presence. Their busy season usually falls between May and July, depending on the region’s climate.
So, whether you’re strolling through an American backyard or exploring a European garden, don’t be surprised to come across these charming June Bugs, adding their unique buzz to the summer symphony.
Japanese Beetle: The Voracious Invaders
Get ready to meet the flashy invaders of our gardens – the Japanese Beetles;
Physical Characteristics:
Japanese Beetles are a sight to behold, with their distinctive features setting them apart from the crowd, even amongst other beetles.
Size, shape, and coloration (how it differs from June Bugs): These voracious eaters are slightly smaller than their June Bug counterparts, measuring around ½ inch in length. What makes them truly stand out is their flashy appearance. Their bodies shine with a metallic green hue, making them look like little gems amidst the foliage. To add to their unique charm, Japanese Beetles flaunt coppery-brown wings, creating a striking contrast.
Unique attributes like metallic sheen and tufts of hair: As if their vibrant colors weren’t enough, Japanese Beetles sport small white tufts of hair along the sides of their abdomen, adding an extra touch of flair to their glamorous look.

Life Cycle and Behavior:
The life of a Japanese Beetle is nothing short of intriguing, but be warned – they can be quite the garden troublemakers.
- Egg-laying habits and favored host plants: Female Japanese Beetles lay their eggs in the soil during the early summer months. They have a particular liking for moist soil, which becomes the ideal nursery for their offspring. When it comes to choosing their favorite plants, Japanese Beetles have a diverse palate and will munch on various plants and trees, making them true connoisseurs of the garden world.
- Larval stages and their effects on plant roots: As grubs, Japanese Beetles are notorious for their destructive tendencies. They feast on grassroots, posing a significant threat to your lawn and garden. Their insatiable hunger can lead to brown patches and weakened vegetation, requiring immediate attention to keep their population in check.
- Adult behaviors and feeding preferences: Once they’ve had their fill of grassroots, the adult Japanese Beetles take flight, searching for their next feast. They have a keen eye for flowers, leaves, and fruits, devouring them with gusto. These insatiable eaters can quickly turn a thriving garden into a battlefield of half-eaten plants.
Japanese Beetles might have arrived in North America as accidental tourists, but they’ve made themselves right at home.
You’ll find them predominantly in the eastern United States and parts of the Midwest. States like Ohio, Indiana, and Virginia are popular hangouts for these flashy invaders. As non-native species, their population has steadily grown, causing concern among gardeners in affected regions.
So, be on the lookout; If you’re in their favorite territories, prepare to face the dazzling and insatiable Japanese Beetles, determined to turn your garden into their own personal buffet. It’s time to take a stand against these voracious invaders.

June Bugs vs. Japanese Beetles: Difference
In the epic showdown of June Bugs vs. Japanese Beetles, the main differences lie in their appearance, behavior, and impact on your garden.
June Bugs boast a reddish-brown hue with fan-like antennae and are less destructive, while Japanese Beetles shine in metallic green with tufts of hair and are voracious plant eaters. Proper identification is crucial for effective management, utilizing natural predators, organic control methods, and eco-friendly practices.
Choose wisely to protect your garden sanctuary and create a harmonious ecosystem. Here’s a tabulated summary of the differences between June Bugs and Japanese Beetles:
| Characteristics | June Bug | Japanese Beetle |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Size | About 1 inch in length | Approximately ½ inch in length |
| Coloration | Reddish-brown with a shiny appearance | Metallic green with coppery-brown wings |
| Antennae | Fan-like antennae | Regular antennae |
| Abdomen | Smooth | White tufts of hair on sides |
| Egg-laying | Early summer in the soil | Early summer in moist soil |
| Preferred Diet | Leaves | Flowers, leaves, and fruits |
| Larval Behavior | Feed on plant roots and organic matter underground | Feed on grassroots, causing lawn and garden damage |
| Geographic Distribution | Common in North America, Europe, and Asia | Predominantly found in the eastern United States and parts of the Midwest |
| Damages | Irregular holes in leaves, particularly at the edges. | Skeletonized leaves, with only the veins remaining. |
| Geographic Distribution | Common in North America, Europe, and Asia | Predominantly found in the eastern United States and parts of the Midwest |
| Geographic Distribution | Common in North America, Europe, and Asia | Predominantly found in the eastern United States and parts of the Midwest |
Tips to Differentiate:
- Size and Color: June Bugs are larger and have a reddish-brown color with a shine, while Japanese Beetles are smaller, sport a metallic green body, and have coppery-brown wings.
- Antennae: Look for the distinct fan-like antennae of June Bugs to identify them, while Japanese Beetles have no such unique feature.
- White Tufts of Hair: Observe the sides of the abdomen – if there are small white tufts of hair, you’re looking at a Japanese Beetle.
- Time of Emergence: June Bugs typically emerge in the warmer months, while Japanese Beetles make their appearance in early summer.
- Feeding Preferences: June Bugs are not as destructive as Japanese Beetles and primarily eat leaves, whereas the latter feed on various plants, including flowers and fruits.
- Location: If you are in the eastern United States or parts of the Midwest, chances are you might encounter Japanese Beetles.
By keeping these pointers in mind, you’ll become a beetle identification expert, allowing you to take appropriate measures to manage these garden visitors effectively. So, next time you spot a beetle, you’ll know if it’s a delightful June Bug or a flashy Japanese Beetle.
Battle of the Beetles: Impact on Plants and Gardens
In the epic clash of June Bugs and Japanese Beetles, it’s essential to understand how each contender affects our precious plants and gardens.
How June Bugs Affect Plants:
While June Bugs may create a gentle buzz in the evening air, their impact on plants is relatively milder compared to their flashy rivals.
As adults, June Bugs primarily feed on leaves and can cause some minor damage. They are often attracted to outdoor lights, which might lead them astray into your home during those warm summer nights. However, their feeding habits are not as destructive as those of Japanese Beetles.
The real concern with June Bugs lies in their larval stage. The C-shaped grubs reside underground, feeding on plant roots and organic matter. While they can potentially disrupt the healthy growth of grass and plants, they are generally less destructive to a well-maintained garden.
Japanese Beetles’ Impact on Vegetation:
Ah, the glamourous Japanese Beetles might dazzle us with their vibrant appearance, but their feeding frenzy can wreak havoc on our green sanctuaries.
As adults, Japanese Beetles are voracious eaters. They have a broad palate, munching on flowers, leaves, and fruits of various plants and trees. This insatiable appetite can lead to severe damage, leaving foliage riddled with holes and plant life severely weakened.
The real trouble, however, lies beneath the surface. Japanese Beetle grubs are notorious for their root-munching tendencies. Feeding on the grassroots can result in brown patches on lawns and impaired growth for garden plants. Infestations can turn a thriving garden into a struggling battleground.
Identifying Damage Caused by Each Beetle:
The key to identifying which beetle is causing the damage lies in the type of destruction observed in your garden.
June Bug Damage:
- Irregular holes in leaves, particularly at the edges.
- Minor leaf damage without severe defoliation.
- Relatively little harm to grass and plants.
Japanese Beetle Damage:
- Skeletonized leaves, with only the veins remaining.
- Severe defoliation of plants and trees, making them appear bare.
- Brown patches on lawns due to root feeding by grubs.

By closely examining the nature of the damage, you can pinpoint the culprit and devise an effective plan to combat the invading beetle forces.
Now that you’re well-equipped with knowledge about their respective impacts, it’s time to take action and defend your garden from the potential onslaught. Remember, a well-identified enemy is halfway defeated. So, keep a keen eye out for signs of damage and tackle these garden invaders head-on with confidence and determination.
Natural Predators and Control Methods
In the never-ending battle against June Bugs and Japanese Beetles, nature has its own army of allies to help us in the fight. Let’s explore the natural predators and eco-friendly control methods to manage these beetle populations without harming the environment.
Natural Predators of June Bugs and Japanese Beetles:
Mother Nature has a way of maintaining balance, and that includes keeping beetle populations in check with the help of some natural predators.
June Bug Predators:
- Birds: Many bird species, such as robins, starlings, and crows, find June Bugs to be a delectable meal.
- Small Mammals: Creatures like moles, shrews, and raccoons feed on June Bug grubs, helping control their underground population.
Japanese Beetle Predators:**
- Birds: Similar to June Bugs, birds play a vital role in controlling Japanese Beetle numbers, with sparrows, grackles, and even chickens, and starlings among the beetle hunters.
- Insects: Beneficial insects like ladybugs, ground beetles, and praying mantises also consider Japanese Beetles a tasty treat.

Organic Control Measures to Manage Beetle Populations:
For those who prefer eco-friendly garden management, several organic methods can help control June Bugs and Japanese Beetles:
- Handpicking: Vigilance is the key; Visit your garden during the morning when beetles are less active, and handpick them off the plants. Drop them into a bucket of soapy water to bid them farewell.
- Neem Oil: Neem oil is a natural insecticide derived from the neem tree. Dilute it with water and spray it on your plants to deter beetles. It won’t harm beneficial insects and can also help with other pests.
- Milky Spore Disease: For Japanese Beetle control, consider introducing milky spore disease. This natural bacterium infects and kills the beetle grubs, effectively reducing their numbers.
- Beneficial Nematodes: These microscopic worms can be applied to the soil to target and kill Japanese Beetle grubs naturally.
- Floating Row Covers: Use lightweight, permeable fabric covers to physically block beetles from accessing your plants. These covers allow sunlight, air, and water to reach the plants while keeping the pests away.
- Companion Planting: Planting certain herbs and flowers near susceptible plants can act as natural repellents. For instance, interplanting garlic, chives, and marigolds can help deter beetles from feasting on your prized plants.
- Diatomaceous Earth: Sprinkle food-grade diatomaceous earth around your plants. This natural substance contains sharp microscopic particles that can pierce the beetles’ bodies, causing dehydration and death.
- Beneficial Insect Attractants: Attracting beneficial insects like parasitic wasps and tachinid flies can help control beetle populations. Plant nectar-rich flowers to encourage these insects to visit your garden.
- Trap Crops: Introduce sacrificial plants that beetles are particularly fond of. By luring the pests away from your main crops, you can minimize the damage to your prized plants.
- Handmade Traps: Create simple traps using empty containers filled with soapy water or a mixture of water and vinegar. Place the traps near your plants to attract and trap the beetles.
- Essential Oil Sprays: Certain essential oils, such as peppermint, clove, or rosemary oil, can be diluted with water and sprayed on plants to repel beetles.
- Nematodes: Beneficial nematodes are microscopic worms that can be applied to the soil to target and control beetle grubs effectively.
- Manual Removal: Conduct regular garden inspections and remove beetles by hand. This method is particularly useful for smaller garden spaces.
- Vigilance: Early detection and intervention are crucial. Regularly monitor your plants for signs of beetle activity, and promptly address any infestations.
By adopting a combination of these organic methods, you can create a balanced and beetle-resistant garden environment. Remember that consistency and persistence are key when using organic control measures. Embracing these eco-friendly techniques will not only help manage beetle populations but also contribute to a healthier and more sustainable garden ecosystem.
Prevention and Protection
Preventing beetle infestations and protecting your garden from the onslaught of June Bugs and Japanese Beetles are essential steps in maintaining a thriving and beautiful outdoor oasis. Let’s explore some effective prevention and protection strategies:
- Healthy Soil Management: Start with the foundation – healthy soil equals healthy plants. Ensure your garden soil is well-draining and rich in organic matter. Healthy plants are better equipped to withstand beetle attacks.
- Crop Rotation: Rotate your crops annually to prevent the buildup of beetle populations in the soil. This disrupts the life cycle of beetles, making it harder for them to find suitable host plants.
- Remove Attractants: Keep your garden free of debris, fallen fruit, and overripe vegetables that might attract beetles. Removing these food sources can discourage them from making themselves at home.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch around plants to deter egg-laying females. Mulch also helps conserve soil moisture and suppress weed growth, which can attract beetles.
- Encourage Natural Predators: Create a welcoming habitat for beneficial insects and birds that prey on beetles. Plant native flowers, shrubs, and trees to attract these natural allies.
- Garden Hygiene: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of beetles and promptly remove any affected leaves or plants. This reduces the attractiveness of your garden to beetles.
- Handpick and Trap: If beetle populations are low, handpick them off your plants or use homemade traps to prevent further damage.
- Physical Barriers: Use physical barriers like floating row covers or netting to shield susceptible plants from beetle feeding.
- Companion Planting: Intercropping plants with natural repellents like garlic, onions, or marigolds can act as a protective shield for vulnerable plants.
- Water Wisely: Avoid overwatering your garden, as damp soil can be an ideal breeding ground for beetle larvae.
- Fall Cleanup: Conduct a thorough fall garden cleanup to remove debris and fallen leaves, which can serve as overwintering sites for beetles.
- Plant-Resistant Varieties: When choosing plants for your garden, opt for beetle-resistant varieties whenever possible.
By combining these prevention and protection strategies, you can create a garden fortress that is less attractive to beetles and more resilient to their attacks.
While it might not be possible to completely eliminate beetles from your garden, implementing these measures will undoubtedly reduce their impact and help you enjoy a flourishing and pest-resistant outdoor sanctuary. Remember, a little proactive planning goes a long way in maintaining a garden paradise
June Bug vs. Japanese Beetle FAQs?
Can June Bugs and Japanese Beetles cause significant harm to my garden?
Both June Bugs and Japanese Beetles can cause damage to your garden, but their impact varies.
- June Bugs: While June Bugs can be a nuisance and may accidentally enter your home during their nighttime flights, their feeding habits are generally not highly destructive to plants. The real concern with June Bugs lies in their larval stage, where the C-shaped grubs feed on plant roots and organic matter underground. Though this can lead to minor damage, it is generally less severe compared to Japanese Beetles.
- Japanese Beetles: These flashy invaders are known for their voracious appetite. As adults, Japanese Beetles feed on flowers, leaves, and fruits, causing severe defoliation and damage to plants. Additionally, their larvae, or grubs, are notorious for feeding on grassroots, potentially resulting in brown patches on lawns and weakened vegetation.
Are these beetles harmful to humans or pets?
No, neither June Bugs nor Japanese Beetles pose direct harm to humans or pets. They are not venomous and do not bite or sting. Their primary focus is on feeding on plant material, not on interacting with humans or animals.
However, keep in mind that some pets may be curious and attempt to eat beetles, which can lead to gastrointestinal upset. To ensure the safety of your pets, it’s best to discourage them from consuming any insects found in the garden.
How can I identify the eggs and larvae of each beetle?
- June Bug Eggs: June Bug eggs are small, white to cream-colored, and oval-shaped. They are typically laid in clusters in the soil, close to the surface. Identifying the eggs might be challenging, as they are often hidden from view, but you may find them while digging in the soil during the early summer months.
- June Bug Larvae (Grubs): June Bug grubs are C-shaped, cream-colored, and have a distinct reddish-brown head capsule. They have six legs and are usually found in the soil, feeding on plant roots and organic matter.
- Japanese Beetle Eggs: Japanese Beetle eggs are tiny, oval-shaped, and white. They are laid in small clusters in the soil, usually near the roots of favored host plants. Identifying the eggs may require careful inspection of the soil around susceptible plants during early summer.
- Japanese Beetle Larvae (Grubs): Japanese Beetle grubs are C-shaped, milky white, and have a brown head capsule. They have three pairs of prominent legs and are commonly found in the soil, feeding on grass roots.
Conclusion
In the battle of the beetles, we’ve learned that June Bugs and Japanese Beetles each have their own unique characteristics and behaviors. June Bugs, with their reddish-brown hue and distinctive fan-like antennae, are less destructive than their flashy counterparts. Japanese Beetles, adorned in metallic green with white tufts of hair, are voracious plant eaters, causing severe damage to foliage and grassroots.
Proper identification is crucial for effective beetle management. Recognizing the eggs, larvae, and adult features of each species allows for targeted control measures.
Natural predators, organic repellents, and eco-friendly practices are powerful allies in protecting your garden from beetle invasions. Encourage beneficial insects, utilize traps, and maintain garden hygiene to deter beetles while maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Choosing eco-friendly control methods over chemical insecticides preserves the well-being of beneficial insects and the environment. Only when necessary should carefully applied insecticides be considered.
Prioritizing the health of your garden and its inhabitants fosters a thriving landscape where you can enjoy the beauty of nature without compromising the balance of the ecosystem.
By embracing responsible gardening practices, you can safeguard your garden from the ravages of beetles and create a flourishing haven for both plants and beneficial creatures.