Are pesky aphids wreaking havoc in your garden, causing distress to your beloved plants? If you’re wondering how to get rid of aphids permanently, you’ve come to the right place! These tiny, sap-sucking insects might seem harmless individually, but their collective presence can lead to disastrous consequences for your precious greens.
Aphids, those minuscule yet bothersome critters, have a knack for multiplying rapidly and can quickly turn a thriving garden into a battlefield of wilting leaves and stunted growth. They’re notorious for sucking the vital juices out of your plants, leaving behind weakened and vulnerable foliage.
Fear not, for we’re here to equip you with an arsenal of effective and eco-friendly methods to bid farewell to these unwelcome intruders once and for all! Say goodbye to temporary fixes and embrace a long-lasting solution that ensures your garden remains aphid-free.
Ready to nurture your plants without the constant fear of aphid attacks? Discover the secrets to get rid of aphids permanently and let your garden flourish like never before. It’s time to reclaim your green sanctuary and put those pesky aphids in their place. Let’s dive into the world of aphid control and regain control over your garden’s destiny.
Understanding Aphids
Aphids, those tiny insects with a knack for causing big trouble, belong to the superfamily Aphidoidea. These soft-bodied pests are usually about 1/16 to 1/8 inch long and come in various colors, including green, yellow, black, brown, and even pink. Despite their diminutive size, aphids can be a formidable force in the garden due to their rapid reproduction rate.
The lifecycle of an aphid is nothing short of fascinating – they undergo both sexual and asexual reproduction. In spring, female aphids give birth to live nymphs without the need for mating.

These nymphs mature into adults in just a few weeks, and the cycle repeats itself. When the population becomes overcrowded or the conditions are unfavorable, winged aphids are born, allowing them to disperse to new plants and start new colonies. This rapid breeding process makes aphids a formidable adversary for gardeners.
Numerous aphid species exist, and each has its favorite plants to feast upon. For instance, the green peach aphid (Myzus persicae) infests a wide range of plants, including peaches, peppers, and tomatoes.
The cabbage aphid (Brevicoryne brassicae) prefers cruciferous vegetables such as cabbage, broccoli, and kale. It’s essential to identify the specific type of aphid infesting your plants to implement targeted control measures effectively.
Signs of Aphid Infestation
Identifying an aphid infestation early is crucial for effective control. Keep a close eye on your plants and watch for these signs that may indicate the presence of aphids:
- Clusters of Tiny Insects: Look for clusters of small, soft-bodied insects on the undersides of leaves, stems, and new shoots. Aphids are typically around 1/16 to 1/8 inch long and come in various colors, such as green, yellow, black, brown, and pink.
- Curling or Distorted Leaves: Aphids puncture plant tissues to feed on sap. As they do so, they can cause leaves to curl, twist, or become misshapen.
- Yellowing Leaves: Prolonged feeding by aphids can lead to yellowing leaves, as the plants’ nutrient supply is diminished.
- Sticky Residue: Aphids excrete a sugary substance called honeydew as they feed. This sticky residue may accumulate on leaves and stems, attracting ants and promoting the growth of sooty mold.
- Ant Presence: Ants are often attracted to the honeydew produced by aphids and may be seen crawling around the infested plants.
- Wilting and Stunted Growth: In severe infestations, plants may exhibit wilting and stunted growth due to significant sap loss.
- Distorted Flowers and Fruits: Aphids feeding on flower buds or developing fruits can cause deformation and affect the quality of flowers and produce.
- Shed Skins: As aphids molt during their growth stages, they leave behind shed exoskeletons on the plant.
- Winged Aphids: In certain conditions, aphids may develop wings, allowing them to disperse to other plants and start new colonies.
- Leaf Curling: Some aphid species induce leaf curling or gall formation, where the plant responds to their feeding by creating abnormal growths.
- Ant-Attendance: Aphids have a unique relationship with ants, where ants “farm” aphids for their honeydew. If you observe ants tending to aphids on your plants, it’s a sign of aphid presence.
Regularly inspect your plants for these signs, especially during warmer months when aphid populations tend to thrive. By identifying and addressing aphid infestations promptly, you can protect your plants and prevent the problem from escalating.

The Damage Caused by Aphids
Aphids, those seemingly innocuous pests, can unleash a world of havoc upon your beloved plants and crops. Understanding the potential harm they cause is essential for taking swift action to protect your greenery.
- Stunted Growth and Reduced Yields: As aphids feed on plant sap, they deprive plants of essential nutrients. This constant nutrient drain leads to stunted growth, weakened stems, and a decline in overall plant health. In agricultural settings, aphid-infested crops often experience reduced yields, affecting farmers’ livelihoods and the availability of fresh produce.
- Deformed and Discolored Leaves: Aphids’ voracious feeding habits can cause leaves to become deformed, curl, or twist. Affected leaves may take on a yellow or brownish hue, indicating their compromised health. Such visual damage can mar the beauty of ornamental plants and disrupt the aesthetic appeal of gardens.
- Distorted Flowers and Fruits: Aphid infestations can lead to deformed flowers and fruits, impacting pollination and reducing the quality of produce. Misshapen fruits can become more susceptible to rot and diseases, further compounding the problem.
- Spread of Plant Diseases: Aphids are not just sap-suckers; they can also act as vectors for various plant viruses. When they feed on infected plants, they can acquire the virus and then transmit it to healthy plants as they move from one host to another. This transmission of viruses can lead to severe diseases, causing extensive damage to entire crops or gardens.
- Weakening Plant Resistance: Aphid feeding weakens the plant’s natural defenses. Plants under aphid attack become more vulnerable to other pests, diseases, and environmental stressors, further compromising their ability to thrive.
The Risks of Leaving Aphids Untreated
Leaving aphids unchecked can lead to a cascade of negative consequences for your garden or crops:
- Rapid Population Growth: Aphids reproduce rapidly through asexual reproduction, meaning they can multiply quickly and establish large colonies on plants in a short period. The longer aphids are left untreated, the more challenging it becomes to control their population.
- Infestation Spread: Aphids can migrate from one plant to another, infesting nearby healthy plants and creating new colonies. Neglecting the problem in one area of your garden may lead to the widespread infestation of other plants.
- Economic Losses: In agricultural settings, aphid infestations can result in significant economic losses due to reduced crop yields and damaged produce.
- Secondary Pests and Diseases: Aphid infestations weaken plants, making them susceptible to attacks from other pests and diseases. This can trigger a chain reaction of additional pest and disease problems, leading to a decline in overall garden health.
- Environmental Impact: Heavy reliance on chemical insecticides to control aphids can harm beneficial insects, disrupt the ecosystem, and contaminate soil and water. Taking a proactive and holistic approach to aphid control is essential for maintaining ecological balance.
The damage caused by aphids can be extensive and far-reaching. To protect your plants, prevent diseases, and maintain a thriving garden, it’s crucial to address aphid infestations promptly and adopt effective, sustainable control measures. A proactive stance will ensure the long-term health and beauty of your garden or crops.
How to Get Rid of Aphids Permanently
When it comes to tackling aphids in your garden, going the natural route not only protects the environment but also ensures the long-term health of your plants. Let’s explore some effective and eco-friendly methods to keep those pesky aphids at bay.
Handpicking:
When facing a limited aphid infestation, handpicking can be a practical and environmentally friendly method to get rid of these pesky pests. This direct approach allows you to physically remove aphids from affected plants, significantly reducing their numbers and preventing further damage.
How Handpicking Works:
- Inspect Regularly: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of aphids. Focus on the undersides of leaves, tender new shoots, and the growing tips of plants, as aphids often prefer these areas.
- Gather Necessary Tools: Arm yourself with a pair of gardening gloves, a bucket of soapy water, and a soft brush or cloth for brushing off aphids gently.
- Start Picking: Gently pick off the aphids from the plants using your fingers or a soft brush. Take care not to crush the aphids, as this may release alarm pheromones that attract more aphids to the area.
- Dispose of Aphids: Drop the collected aphids directly into the bucket of soapy water. The soapy water will drown the aphids and prevent them from crawling back onto the plants
- Repeat as Needed: Continue the handpicking process regularly, especially during the growing season when aphid populations are at their peak. Consistency is key to ensuring successful control.
Tips for Effective Handpicking:
- Handpick in the early morning or late evening when aphids are less active.
- Focus on the areas where aphids are concentrated or where new infestations are appearing.
- Check the undersides of leaves carefully, as aphids often hide there.
- Encourage children to participate, making handpicking a fun and educational family activity.
- Combine handpicking with other natural control methods, like attracting beneficial insects, for better results.
By combining handpicking with preventive strategies, you can maintain a healthy and aphid-resistant garden, ensuring your plants thrive without the threat of aphid infestations.
Using Insecticidal Soaps:
Insecticidal soaps offer an environmentally friendly and effective method to combat aphid infestations. These soaps contain fatty acids that target soft-bodied insects like aphids, disrupting their cell membranes and leading to dehydration and death.
Insecticidal soaps are less toxic to beneficial insects, plants, and humans, making them a preferred choice for aphid control. You can make an insecticidal soap or buy it from an online store to save time.

How Insecticidal Soaps Work:
- Select the Right Product: Purchase a reputable insecticidal soap product from a garden center or nursery. Ensure that the soap is specifically formulated for use on plants and aphids.
- Prepare the Solution: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to prepare the insecticidal soap solution. Typically, you’ll need to mix a specified amount of the soap concentrate with water in a sprayer.
- Test a Small Area: Before applying the solution to the entire plant, test it on a small section to check for any adverse reactions. This step is especially crucial for sensitive or delicate plants.
- Apply the Solution: Spray the insecticidal soap solution directly on the aphids, covering both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves. The soap works by suffocating the aphids, so thorough coverage is essential.
- Repeat if Necessary: If the aphid population persists, reapply the insecticidal soap according to the product’s recommended frequency. Repeat applications may be needed to achieve effective control.

Tips for Effective Use of Insecticidal Soaps:
- Timing: Apply insecticidal soap during the cooler parts of the day, like early morning or late afternoon, to minimize the risk of leaf damage.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Avoid applying the solution in direct sunlight or during hot temperatures, as this may cause leaf burn.
- Thorough Coverage: Ensure complete coverage of the aphids and affected plant parts, including new growth and tender shoots.
- Follow Instructions: Always read and follow the instructions on the insecticidal soap product label. Using more than the recommended concentration can harm plants and beneficial insects.
- Consistent Application: Aphids reproduce quickly, so regular and consistent applications are crucial to maintain control.
By integrating insecticidal soaps into a holistic approach to aphid control, you can effectively manage aphid populations while preserving the health and balance of your garden ecosystem.
Pruning:
Pruning is an effective method to control aphids and prevent their infestation from spreading to other parts of the plant or nearby plants. By strategically removing affected plant parts, you can limit the aphid population and enhance your plant’s ability to recover and resist future attacks.
How Pruning Works:
- Identify Infested Areas: Regularly inspect your plants for aphid infestations. Look for clusters of aphids, distorted leaves, and other signs mentioned earlier.
- Prepare Pruning Tools: Use clean and sharp pruning shears or scissors to avoid damaging the plant while cutting. It’s essential to sanitize your pruning tools between plants to prevent the potential spread of diseases.
- Cut Infested Plant Parts: Carefully prune the infested areas, such as heavily infested leaves, stems, or flowers. Remove these parts by making clean cuts just above a leaf node or branch junction.
- Dispose of Pruned Material: Collect the pruned material and dispose of it away from the garden. Do not compost aphid-infested plant parts, as the aphids may continue to thrive in the compost pile.
- Monitor and Repeat: Keep a close eye on your plants after pruning to ensure that the aphid population doesn’t rebound. If you notice new infestations, promptly repeat the pruning process.
Tips for Effective Pruning:
- Prune during the cooler parts of the day, like early morning or late evening, to reduce stress on the plant.
- Use smooth, clean cuts to promote rapid healing and prevent entry points for pathogens.
- Avoid excessive pruning, as this can stress the plant. Focus on removing heavily infested areas and any dead or diseased parts.
- If dealing with severe infestations, consider pruning only a portion of the affected plant initially, allowing it to recover before further pruning.
Remember, pruning is a proactive measure to control aphids, especially when dealing with localized infestations. By practicing this method alongside other preventive strategies, you can create a balanced ecosystem in your garden, ensuring the long-term health and well-being of your plants.
Using Neem Oil:
Neem oil is derived from the seeds of the neem tree (Azadirachta indica) and is well-known for its insecticidal properties. It acts as both a repellent, deterring aphids from infesting plants, and an insecticide, disrupting their growth and reproductive cycles.
Neem oil is considered safe for beneficial insects, mammals, and humans, making it an eco-friendly option for aphid control. There are ready-to-spray neem oil in the market and you can also make yours and apply as you need to keep your garden safe for long.

How Neem Oil Works Against Aphids:
- Repellent Action: The strong smell of neem oil repels aphids, discouraging them from landing and feeding on plants.
- Insecticidal Action: Neem oil contains compounds that disrupt the hormonal system of aphids, affecting their feeding and reproduction.
DIY Homemade Neem Oil Spray – Step-by-Step Guide:
Ingredients:
- Pure neem oil
- Mild liquid soap (e.g., Castile soap)
- Water
Equipment:
- A clean empty spray bottle
Instructions:
- Measure Neem Oil: Start by measuring the neem oil. For a 1% neem oil solution (suitable for mild infestations and preventive use), use 1 teaspoon of neem oil. For a 2% solution (for moderate infestations), use 2 teaspoons. Avoid using higher concentrations as they can harm plants.
- Add Mild Liquid Soap: Add a few drops of mild liquid soap to the measured neem oil. The soap acts as an emulsifier, helping the oil mix with water.
- Mix the Ingredients: Mix the neem oil and soap thoroughly until well combined. This step is crucial to prevent the neem oil from separating from the water when making the spray.
- Prepare the Spray Bottle: Fill the empty spray bottle with water, leaving some space at the top for the neem oil mixture.
- Add the Neem Oil Mixture: Pour the Neem oil and soap mixture into the water-filled spray bottle.
- Shake Vigorously: Secure the spray bottle cap and shake the bottle vigorously for a few minutes to ensure proper emulsification.
How to Apply Neem Oil Spray:
- Test a Small Area: Before using the neem oil spray on the entire plant, test it on a small section of the plant to check for any adverse reactions.
- Spray the Plants: Thoroughly spray the neem oil solution on all parts of the affected plant, including the upper and lower leaf surfaces.
- Apply Early Morning or Late Afternoon: Apply the neem oil spray during the cooler parts of the day, like early morning or late afternoon, to avoid leaf burn in direct sunlight.
- Repeat as Needed: For effective aphid control, reapply the neem oil spray every 7-14 days, or as recommended by the severity of the infestation.
By utilizing homemade neem oil spray and integrating it into a holistic aphid control approach, you can protect your plants and create a balanced, healthy garden ecosystem.
Using Horticultural Oil:
Horticultural oil, also known as dormant oil or summer oil, is a natural and non-toxic solution for managing aphids and other soft-bodied insects.
Derived from mineral or plant-based oils, horticultural oil works by suffocating and smothering aphids, disrupting their respiration and preventing further infestations.
This method is particularly effective against overwintering aphid eggs and nymphs, making it an essential part of your aphid control strategy.

How Horticultural Oil Works Against Aphids:
- Smothering Action: When sprayed on aphids, horticultural oil forms a thin film that coats their bodies, blocking their breathing pores and causing suffocation.
- Disruption of Life Stages: Horticultural oil targets the overwintering eggs and nymphs of aphids, interrupting their life cycle and reducing future generations.
Applying Horticultural Oil – Step-by-Step Guide:
Ingredients:
- Horticultural oil (follow the product label for recommended concentration)
- Water
Equipment:
- A clean empty spray bottle or a garden sprayer
Instructions:
- Choose the Right Time: Apply horticultural oil when the temperature is between 40°F to 85°F (4°C to 29°C) and when no risk of frost is expected within 24 hours.
- Prepare the Solution: Dilute the horticultural oil as per the manufacturer’s instructions. The recommended concentration typically ranges from 1% to 2%.
- Prepare the Spray Equipment: Fill the spray bottle or garden sprayer with the diluted horticultural oil solution.
- Shake Well: Thoroughly shake the spray bottle or garden sprayer to ensure the oil is well-mixed with water.
- Test a Small Area: Before treating the entire plant, test the horticultural oil on a small section to check for any adverse reactions, especially if applied to sensitive or delicate plants.
- Spray the Plants: Spray the horticultural oil solution on all parts of the affected plant, making sure to cover the leaves and stems thoroughly.
- Even Coverage: Ensure even coverage, paying attention to the undersides of leaves, where aphids often congregate.
- Apply in the Right Conditions: Apply the horticultural oil on a calm day to prevent drift, and avoid spraying when the plant is under stress (e.g., drought or heat stress).
By incorporating horticultural oil into your aphid control routine and combining it with preventive strategies, you can maintain healthy, aphid-resistant plants and promote a thriving garden ecosystem.
Companion Planting:
Companion planting is an age-old gardening technique that involves strategically planting certain plants together to enhance growth, repel pests, and attract beneficial insects.
When it comes to aphid control, companion planting can play a crucial role in deterring aphids and creating a harmonious garden ecosystem.
How Companion Planting Works Against Aphids:
- Natural Repellents: Some plants naturally emit strong scents or compounds that repel aphids. Companion planting these repellent plants near susceptible crops creates a protective barrier against aphid infestations.
- Beneficial Insects: Certain companion plants attract beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps, which are natural predators of aphids. By providing these predators with a nearby food source, they are encouraged to stay and help control aphid populations.
Companion Planting Strategies to Deter Aphids:
- Marigolds (Tagetes spp.): Marigolds exude a pungent odor that repels aphids and other pests. Plant marigolds around susceptible crops like tomatoes, peppers, and beans to deter aphids from settling in.
- Mint (Mentha spp.) and Chives (Allium schoenoprasum): The strong aromatic scent of mint and chives acts as a natural deterrent to aphids. Plant these herbs among your vegetables or flowers to create an unappealing environment for aphids.
- Nasturtiums (Tropaeolum majus): Nasturtiums are not only beautiful and edible flowers but also act as a trap crop for aphids. They attract aphids away from other plants, drawing them to their leaves instead.
- Garlic (Allium sativum): The pungent aroma of garlic is an effective aphid repellent. Plant garlic near roses, tomatoes, or fruit trees to discourage aphids from infesting these plants.
- Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare): Fennel not only repels aphids but also attracts beneficial insects like ladybugs. Plant fennel near crops that are susceptible to aphid attacks.
Companion Planting Guidelines:
- Placement: Plant companion plants around your vulnerable crops, forming a border or intermingling them throughout the garden beds.
- Diversity: Use a diverse range of companion plants to create a balanced and attractive environment for beneficial insects.
- Observe and Adjust: Monitor the effectiveness of companion planting in your garden. If you notice persistent aphid infestations, consider adjusting your companion planting strategy or trying additional methods.
By embracing companion planting alongside other preventive measures and control methods, you can foster a thriving, pest-resistant garden while minimizing the need for chemical interventions. Harness the power of plant partnerships and maintain a garden ecosystem that is in harmony with nature.
Attracting Beneficial Insects:
Attracting beneficial insects is a proactive and eco-friendly approach to combat aphids in your garden. Beneficial insects are natural predators that prey on aphids and other garden pests, helping to keep their populations in check.
By creating a welcoming habitat for these beneficial insects, you can establish a natural balance in your garden and reduce the need for chemical pesticides.
How Attracting Beneficial Insects Works Against Aphids:
- Natural Predators: Beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, parasitic wasps, and hoverflies are voracious aphid predators. They feed on aphids at various life stages, reducing their numbers and preventing infestations.
- Biological Control: By attracting these beneficial insects to your garden, you encourage a natural form of biological control, where predators maintain aphid populations at manageable levels.
Guidelines to Attract Beneficial Insects:
- Plant Nectar and Pollen-Rich Flowers: Flowers that provide nectar and pollen serve as valuable food sources for beneficial insects. Choose a diverse range of flowering plants that bloom at different times of the year to sustain insects throughout the seasons. Examples of attractive flowers include:
- Sunflowers (Helianthus spp.)
- Daisies (Asteraceae family)
- Yarrow (Achillea millefolium)
- Lavender (Lavandula spp.)
- Coneflowers (Echinacea spp.)
- Goldenrod (Solidago spp.)
- Create Shelter and Habitat: Beneficial insects require places to shelter, rest, and lay eggs. Consider incorporating the following features into your garden:
- Bug hotels: Build or buy bug hotels, which provide crevices and spaces for beneficial insects to hide and nest.
- Rocks and logs: Leave some rocks and logs around the garden to create hiding spots and homes for insects.
- Leaf litter: Allow a layer of leaf litter to accumulate in some areas, providing shelter for overwintering insects.
- Minimize Pesticide Use: Reduce or eliminate the use of chemical pesticides, as they can harm beneficial insects. Opt for natural control methods to preserve the predator-prey balance.
- Water and Hydration: Provide a water source, such as a shallow dish with pebbles, for beneficial insects to drink from and maintain hydration.
- Avoid Monoculture: Plant a variety of crops and flowers rather than a single type of plant. Monoculture can attract and sustain large populations of pests, making it challenging for beneficial insects to control them effectively.
Patience and Observation:
Attracting beneficial insects may take time, and the presence of predators may fluctuate throughout the year. Be patient and observe changes in insect populations. As your garden becomes more hospitable to beneficial insects, you’ll notice fewer aphids and a healthier, balanced ecosystem.
By embracing the power of beneficial insects and integrating them into a holistic aphid control strategy, you can maintain a thriving garden ecosystem while reducing the need for chemical interventions. Embrace nature’s allies and let them do the hard work of aphid control for you
Using Aphid Traps:
Aphid traps are an effective and low-impact method to monitor and control aphid populations in your garden. These traps attract aphids and capture them, preventing further infestations and providing valuable information about the severity of the aphid problem. Aphid traps work by luring aphids with attractive scents or colors, providing a targeted and eco-friendly means of managing these pests.
How Aphid Traps Work Against Aphids:
- Attractant Lures: Aphid traps use specific scents or colors that mimic aphid host plants or appeal to the pests’ senses. The aphids are drawn to the trap, leaving your valuable crops unharmed.
- Population Monitoring: By regularly checking the traps, you can gauge the severity of aphid infestations and take action before the situation becomes overwhelming.

Types of Aphid Traps:
- Yellow Sticky Traps: These traps consist of yellow surfaces coated with a sticky adhesive. Yellow attracts aphids, and when they land on the trap, they get stuck, preventing them from reaching your plants.
- Pheromone Traps: Pheromones are natural chemicals that aphids use for communication and mating. Pheromone traps release synthetic aphid pheromones to lure aphids, which are then trapped or captured.
- Scented Traps: Scented traps utilize attractive scents, such as floral or fruity aromas, to entice aphids and draw them away from your plants.
Applying Aphid Traps – Step-by-Step Guide:
- Determine the Number of Traps: Assess the size of your garden and the severity of the aphid problem to decide on the number of traps needed. For small gardens, a few traps may suffice, while larger areas may require several traps distributed evenly.
- Placement: Position the traps near susceptible plants or areas where aphids are frequently observed. Hang or attach the traps at plant height for the best results.
- Install the Traps: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to set up the traps correctly. For sticky traps, remove the protective covering from the adhesive surface. For pheromones or scented traps, activate or insert the lure as directed.
- Regular Monitoring: Check the traps regularly, at least once a week, to assess aphid activity. Count the number of aphids caught in each trap to gauge the severity of the infestation.
- Replace or Clean Traps: Depending on the type of trap used, you may need to replace sticky traps or refresh the lures periodically to ensure their effectiveness.
By incorporating aphid traps into a holistic approach to aphid control, you can effectively monitor and manage aphid populations while minimizing the need for chemical interventions. Use these traps to your advantage and keep your garden free from harmful aphid infestations!
Blast with water:
Using a water spray to get rid of aphids is a natural and straightforward approach that can yield significant results, especially for small to moderate infestations. The force of the water dislodges and physically removes aphids from your plants, effectively deterring them and preventing further damage.
How Water Spray Works Against Aphids:
- Physical Removal: The water spray dislodges aphids from plant surfaces, causing them to fall off the plant. This helps break the aphids’ feeding cycle and reduces their numbers on your plants.
- Interferes with Pheromone Communication: The water spray may disrupt the aphids’ ability to communicate using pheromones, making it harder for them to locate and target plants.
Applying Water Spray – Step-by-Step Guide:
- Prepare the Water Spray: Fill a clean spray bottle or garden hose sprayer with water. It’s best to use room temperature water, as very cold or hot water may harm the plants.
- Test Water Pressure: If using a garden hose sprayer, test the water pressure to ensure it is not too forceful. A gentle mist or spray setting is preferable to avoid damaging delicate plant tissues.
- Inspect the Plants: Identify the areas with aphids, focusing on the undersides of leaves and tender new shoots, as aphids tend to congregate there.
- Spray the Aphids: Aim the water spray directly at the aphids, targeting the infested areas. Use enough pressure to dislodge the aphids, but be gentle to avoid damaging the plants.
- Repeat as Needed: Regularly inspect your plants and repeat the water spray treatment as necessary, especially after rain or if you notice new aphid infestations.
Tips for Effective Water Spray Application:
- Timing: Apply the water spray in the morning or early evening when temperatures are cooler and the plants have time to dry before nightfall. Wet leaves in the evening can promote the growth of fungal diseases.
- Consistency: For effective control, be consistent in applying the water spray. Regularly inspect your plants, especially during the growing season, when aphid populations are most active.
- Follow-Up Measures: After spraying, consider introducing natural predators like ladybugs or lacewings to maintain long-term aphid control.
By using water spray in combination with preventive strategies, you can effectively manage aphids without resorting to chemical pesticides. Embrace this simple and eco-friendly method to keep your garden healthy and aphid-free!
Using Essential Oil Sprays
Essential oil sprays offer a natural and aromatic solution to deter and repel aphids from your plants. These potent plant extracts contain compounds that are unpleasant to aphids, making them an effective and environmentally friendly option for aphid control. When used correctly, essential oil sprays can help protect your garden and keep aphids at bay.
How Essential Oil Sprays Work Against Aphids:
- Repellent Action: The strong scents of certain essential oils, like peppermint, rosemary, and neem, are highly unappealing to aphids. When sprayed on plants, these scents deter aphids from landing and feeding.
- Masking: Essential oils can mask the scent of aphid host plants, making it harder for aphids to locate and target the plants they prefer.
Creating an Essential Oil Spray – Step-by-Step Guide:
Ingredients:
- Distilled water
- Essential oil of choice (e.g., peppermint, rosemary, neem)
- Mild liquid soap (e.g., Castile soap) or vegetable oil (optional)
Equipment:
- A clean empty spray bottle
Instructions:
- Select the Essential Oil: Choose a suitable essential oil known for its aphid-repelling properties. Peppermint, rosemary, neem, and eucalyptus are popular choices.
- Measure the Essential Oil: For a 32-ounce (1-liter) spray bottle, add approximately 10-15 drops of essential oil. Adjust the number of drops based on the size of your spray bottle and the strength of the scent.
- Add Water: Fill the spray bottle with distilled water, leaving some space at the top for shaking.
- Optional: Add Soap or Oil: For better adhesion to plant surfaces, you can add a few drops of mild liquid soap or vegetable oil to the spray bottle. This helps the essential oil blend with the water.
- Shake Well: Secure the spray bottle cap and shake the bottle vigorously to thoroughly mix the ingredients.
Applying the Essential Oil Spray:
- Test a Small Area: Before using the essential oil spray on the entire plant, test it on a small section to check for any adverse reactions, especially if applied to sensitive or delicate plants.
- Spray the Plants: Apply the essential oil spray to the entire plant, making sure to cover both the upper and lower leaf surfaces. Concentrate on areas where aphids are most likely to congregate.
- Reapply as Needed: Reapply the essential oil spray every 7-10 days, or as necessary, especially after rain or if you notice new aphid activity.
Tips for Effective Use of Essential Oil Sprays:
- Use a different essential oil in the rotation if possible, as aphids can become accustomed to certain scents over time.
- Avoid spraying essential oils on open flowers, as it may deter beneficial pollinators.
- Essential oil sprays are most effective as a preventive measure or for mild aphid infestations. For severe infestations, consider using other control methods in combination with essential oils.
By using essential oil sprays alongside other preventive strategies, you can effectively deter aphids and maintain a thriving, pest-resistant garden without relying on chemical pesticides. Embrace the power of essential oils and enjoy the benefits of a naturally protected garden.
Using Garlic and Chili Spray
Garlic and chili spray is a powerful homemade remedy to deter and control aphids in your garden. Both garlic and chili contain natural compounds that repel aphids and other pests, making this spray an effective, eco-friendly, and affordable solution for aphid control.
How Garlic and Chili Spray Works Against Aphids:
- Repellent Properties: Garlic and chili contain strong odors and compounds that are unpleasant to aphids. When sprayed on plants, these scents act as a deterrent, making the plants less attractive to aphids.
- Contact Irritant: The active compounds in garlic and chili can cause discomfort to aphids when they come into direct contact with the spray, discouraging them from feeding on the treated plants.
Creating Garlic and Chili Spray – Step-by-Step Guide:
Ingredients:
- 2-3 bulbs of fresh garlic
- 2-3 fresh chili peppers
- 1 quart (1 liter) of water
- Mild liquid soap (e.g., Castile soap) or vegetable oil (optional)
Equipment:
- Blender or food processor
- A clean empty spray bottle
Instructions:
- Prepare Garlic and Chili: Peel the garlic cloves and remove the seeds from the chili peppers. The seeds contain most of the heat, so removing them will make the spray milder.
- Blend the Ingredients: In a blender or food processor, combine the garlic cloves, chili peppers, and water. Blend until you have a smooth, consistent mixture.
- Strain the Mixture: Pour the blended mixture through a fine mesh strainer to remove any large particles. This step prevents clogging of the spray nozzle.
- Optional: Add Soap or Oil: For better adhesion to plant surfaces, you can add a few drops of mild liquid soap or vegetable oil to the strained mixture. This helps the spray stick to the plants.
- Transfer to Spray Bottle: Pour the strained mixture into a clean spray bottle, leaving some space at the top for shaking.
- Shake Well: Secure the spray bottle cap and shake the bottle vigorously to ensure the ingredients are well mixed.
Applying Garlic and Chili Spray:
- Test a Small Area: Before applying the spray to the entire plant, test it on a small section to check for any adverse reactions, especially if applying to sensitive or delicate plants.
- Spray the Plants: Apply the garlic and chili spray to the entire plant, covering both the upper and lower leaf surfaces. Focus on areas where aphids are most likely to congregate.
- Reapply as Needed: Reapply the spray every 7-10 days, or as necessary, especially after rain or if you notice new aphid activity.
Tips for Effective Use of Garlic and Chili Spray:
- Wear gloves when handling chili peppers to avoid irritation, and wash your hands thoroughly afterward.
- Garlic and chili spray are most effective as a preventive measure or for mild aphid infestations. For severe infestations, consider using other control methods in combination with this spray.
- Avoid spraying on open flowers, as it may deter beneficial pollinators.
By using garlic and chili spray alongside other preventive strategies, you can effectively deter aphids and maintain a thriving, pest-resistant garden without relying on chemical pesticides. Embrace the power of natural remedies and enjoy the benefits of a naturally protected garden.
Use Diatomaceous Earth
Diatomaceous Earth (DE) is a natural, fine powder made from the fossilized remains of diatoms, a type of hard-shelled algae. It is a safe and effective method for controlling aphids and other soft-bodied pests in your garden.
DE works by physically damaging the outer waxy layer of insects, causing them to dehydrate and die. It is a non-toxic and eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides.
How Diatomaceous Earth Works Against Aphids:
- Abrasive Action: Diatomaceous Earth has microscopic sharp edges that pierce the soft bodies of aphids. When aphids come into contact with DE, it causes small cuts, leading to the loss of body fluids and eventual dehydration.
- Desiccation: DE absorbs the protective waxy layer on the exoskeleton of aphids, which disrupts their ability to retain moisture. As a result, aphids dry out and die.

Applying Diatomaceous Earth – Step-by-Step Guide:
Ingredients:
- Food-grade Diatomaceous Earth (Ensure it is labeled as “food-grade” for safe use around plants and beneficial insects.)
Equipment:
- Handheld duster or a small garden sprayer
Instructions:
- Choose the Right Time: Apply Diatomaceous Earth when the weather is dry and there is little to no wind. Avoid application during rain or immediately after watering, as it can reduce the effectiveness of DE.
- Wear Protective Gear: Wear a dust mask and gloves when handling Diatomaceous Earth to avoid inhaling the fine particles
- Inspect the Plants: Identify the areas with aphids, focusing on the undersides of leaves and tender new shoots, as aphids tend to congregate there.
- Apply Diatomaceous Earth: Dust a light, even layer of Diatomaceous Earth on the infested plants. Pay special attention to the areas with the highest aphid activity.
- Reapply as Needed: Reapply Diatomaceous Earth after rain or if you notice new aphid activity. DE loses effectiveness when wet, so it may need replenishing.
Tips for Effective Use of Diatomaceous Earth:
- Diatomaceous Earth remains effective as long as it is dry. Reapply after heavy rainfall or if the garden is watered heavily.
- Avoid excessive dusting, as a thick layer of DE may impede the movement of beneficial insects like ladybugs.
By using Diatomaceous Earth alongside other preventive strategies, you can effectively control aphids and maintain a healthy, pest-resistant garden without relying on chemical pesticides. Embrace the natural power of Diatomaceous Earth and enjoy the benefits of a thriving, aphid-free garden.
Using Vinegar:
A vinegar solution is a simple and readily available remedy for deterring and controlling aphids in your garden. Vinegar contains acetic acid, which has natural insecticidal properties and can disrupt aphids’ feeding and reproduction. It is a safe and non-toxic option that can be used as a preventive measure or for managing mild aphid infestations.
How Vinegar Solution Works Against Aphids:
- Deters Aphids: The strong smell and taste of vinegar are unpleasant to aphids, making treated plants less attractive to these pests.
- Contact Spray: Direct application of the vinegar solution can damage aphids’ soft bodies and deter them from feeding on the treated plants.
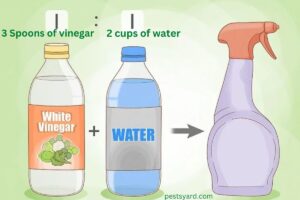
Creating Vinegar Solution – Step-by-Step Guide:
Ingredients:
- White vinegar or apple cider vinegar
- Water
- Mild liquid soap (e.g., Castile soap) or vegetable oil (optional)
Equipment:
- A clean empty spray bottle
Instructions:
- Choose the Vinegar: Use white vinegar or apple cider vinegar for the solution. White vinegar has a higher acetic acid content and may be slightly more effective.
- Mix the Solution: In a clean spray bottle, combine equal parts of vinegar and water. For example, 1 cup of vinegar and 1 cup of water.
- Optional: Add Soap or Oil: To improve the solution’s effectiveness and adhesion to plant surfaces, add a few drops of mild liquid soap or vegetable oil to the spray bottle. This helps the vinegar stick to the plants.
- Shake Well: Secure the spray bottle cap and shake the mixture well to ensure the ingredients are thoroughly mixed.
Applying Vinegar Solution:
- Test a Small Area: Before applying the vinegar solution to the entire plant, test it on a small section to check for any adverse reactions, especially if applying it to sensitive or delicate plants.
- Spray the Plants: Apply the vinegar solution to the entire plant, making sure to cover both the upper and lower leaf surfaces. Focus on areas where aphids are most likely to congregate.
- Reapply as Needed: Reapply the vinegar solution every 7-10 days, or as necessary, especially after rain or if you notice new aphid activity.
Tips for Effective Use of Vinegar Solution:
- Use the vinegar solution as a preventive measure or for mild aphid infestations. For severe infestations, consider using other control methods in combination with vinegar spray.
- Avoid spraying the solution on open flowers, as it may deter beneficial pollinators.
By using vinegar solutions alongside other preventive strategies, you can effectively deter aphids and maintain a thriving, pest-resistant garden without relying on chemical pesticides. Embrace the natural power of vinegar and enjoy the benefits of an aphid-free garden.
Apply Alcohol Spray
An alcohol spray is a simple and practical solution for controlling aphids in your garden. Isopropyl alcohol or rubbing alcohol is a potent desiccant that can effectively kill aphids on contact. It is a non-toxic and readily available option for managing aphid infestations, particularly for small to moderate pest populations.
How Alcohol Spray Works Against Aphids:
- Contact Spray: Alcohol acts as a desiccant, removing the protective waxy layer on aphids’ exoskeletons. When sprayed directly on aphids, it causes them to dehydrate and die.
- Effective Against Soft-Bodied Pests: Aphids have soft bodies, making them particularly susceptible to the dehydrating effects of alcohol.
Applying Alcohol Spray – Step-by-Step Guide:
Ingredients:
- Isopropyl alcohol (rubbing alcohol) with a concentration of 70% or higher
- Water
- Mild liquid soap (e.g., Castile soap) or vegetable oil (optional)
Equipment:
- A clean empty spray bottle
Instructions:
- Choose the Alcohol: Use isopropyl alcohol with a concentration of 70% or higher. Lower concentrations may not be as effective against aphids.
- Mix the Solution: In a clean spray bottle, combine equal parts of alcohol and water. For example, 1 cup of alcohol and 1 cup of water.
- Optional: Add Soap or Oil: To improve the solution’s effectiveness and adhesion to plant surfaces, add a few drops of mild liquid soap or vegetable oil to the spray bottle. This helps the alcohol stick to the plants.
- Shake Well: Secure the spray bottle cap and shake the mixture well to ensure the ingredients are thoroughly mixed.
Applying Alcohol Spray:
- Test a Small Area: Before applying the alcohol spray to the entire plant, test it on a small section to check for any adverse reactions, especially if applying it to sensitive or delicate plants.
- Spray the Plants: Apply the alcohol spray to the entire plant, focusing on areas with the highest aphid activity, such as the undersides of leaves and tender new shoots.
- Reapply as Needed: Reapply the alcohol spray every 7-10 days, or as necessary, especially after rain or if you notice new aphid activity.
Tips for Effective Use of Alcohol Spray:
- Use the alcohol spray as a spot treatment for localized aphid infestations or for managing small to moderate populations.
- Avoid spraying the solution on open flowers, as it may deter beneficial pollinators.
By using alcohol spray alongside other preventive strategies, you can effectively control aphids and maintain a thriving, pest-resistant garden without relying on chemical pesticides. Embrace this natural and practical method and enjoy the benefits of an aphid-free garden.
Reflective Mulch
Reflective mulch is a lesser-known yet effective method for deterring aphids and other insect pests in your garden. This innovative technique involves using mulch with reflective properties to create an environment that is unattractive to aphids. By implementing reflective mulch, you can significantly reduce aphid infestations and promote healthier plant growth.
How Reflective Mulch Works Against Aphids:
- Disorientation: Reflective mulch disorients aphids by reflecting sunlight and creating an unfamiliar environment. This can deter aphids from settling on the plants, reducing their feeding activity.
- Confusion and Avoidance: The shiny surface of reflective mulch may confuse aphids, making it harder for them to locate and target host plants. As a result, aphids may avoid laying eggs or forming colonies on plants covered with reflective mulch.
Applying Reflective Mulch – Step-by-Step Guide:
Materials:
- Reflective mulch material (aluminum-coated, metallic, or white plastic mulch)
Instructions:
- Choose the Reflective Mulch: Select a suitable reflective mulch material, such as aluminum-coated, metallic, or white plastic mulch. These types of mulch have reflective surfaces that effectively deter aphids.
- Prepare the Soil: Prepare the soil in your garden beds by removing weeds and debris and ensuring it is well-drained.
- Install the Reflective Mulch: Lay the reflective mulch on the soil surface around the base of your plants. Make sure to cover the root zones and extend the mulch a few inches beyond the plant canopy.
- Secure the Mulch: Use garden staples or weights to secure the edges of the reflective mulch and prevent it from being blown away by wind.
- Monitor and Maintain: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of aphids and maintain the reflective mulch by adjusting and replacing as needed.
Tips for Effective Use of Reflective Mulch:
- Reflective mulch is most effective as a preventive measure or in combination with other aphid control methods. For severe infestations, consider using other control techniques in addition to reflective mulch.
- Combine reflective mulch with other deterrents like companion planting and attracting beneficial insects to create a more comprehensive aphid management strategy.
By incorporating reflective mulch into your garden, you can deter aphids and create a less favorable environment for these pests. Combined with other preventive strategies, reflective mulch can contribute to the health and vibrancy of your garden by reducing aphid damage and promoting successful plant growth. Enjoy the benefits of this innovative technique and maintain an aphid-free garden with minimal effort.

Use Beneficial Nematodes
Beneficial nematodes are microscopic, soil-dwelling organisms that can serve as effective biological control agents for aphids and other garden pests.
These beneficial nematodes are harmless to plants, animals, and humans, making them an eco-friendly and safe option for controlling aphid infestations. When applied correctly, beneficial nematodes can significantly reduce aphid populations and keep your garden thriving.
How Beneficial Nematodes Work Against Aphids:
- Parasitic Activity: Beneficial nematodes are parasitic to insects, including aphids. They enter the bodies of aphids through natural openings or through their soft exoskeletons. Once inside, the nematodes release bacteria that kill the aphids from within.
- Continued Reproduction: After killing the aphids, beneficial nematodes reproduce inside the aphid cadavers, producing new generations of nematodes that can seek out and infect more aphids.
Applying Beneficial Nematodes – Step-by-Step Guide:
Materials:
- Beneficial nematodes (Ensure you purchase nematodes specifically formulated for aphid control.)
- Watering can or garden sprayer
Instructions:
- Choose the Right Nematodes: Purchase beneficial nematodes that are specifically designed for aphid control. Different nematode species target different pests, so it’s essential to get the correct ones for aphids.
- Prepare the Nematodes: Follow the instructions provided by the supplier to prepare the Nematodes for application. This may involve mixing them with water to create a suspension.
- Moisten the Soil: Before applying the nematodes, moisten the soil in the target area. This helps the nematodes move effectively through the soil and locate their aphid prey.
- Apply the Nematodes: Use a watering can or garden sprayer to apply the nematode suspension to the soil around the infested plants. Ensure thorough coverage of the affected areas.
- Keep Soil Moist: After application, keep the soil consistently moist for several days to support the nematodes’ movement and activity.
Tips for Effective Use of Beneficial Nematodes:
- Apply nematodes in the early morning or late evening when temperatures are cooler. High temperatures and direct sunlight can harm nematodes.
- Avoid applying chemical pesticides before or after nematode application, as they may harm the beneficial nematodes.
By using beneficial nematodes alongside other preventive strategies, you can effectively control aphids and maintain a healthy, pest-resistant garden without relying on chemical pesticides. Embrace the power of nature’s pest control and enjoy the benefits of an aphid-free garden with the help of these microscopic but mighty allies.
Insecticidal Plants
Insecticidal plants, also known as repellent or trap crops, are certain plant species that possess natural compounds or odors that deter aphids and other insect pests.
These plants can be strategically integrated into your garden to create an inhospitable environment for aphids and help protect your valuable crops from infestations.
How Insecticidal Plants Work Against Aphids:
- Repellent Properties: Insecticidal plants release specific chemicals or fragrances that are unpleasant to aphids. These compounds act as natural repellents, discouraging aphids from approaching the plants and laying eggs.
- Trap Crops: Some insecticidal plants can act as “trap crops,” attracting aphids away from your main crops. Aphids prefer these trap crops, which divert their attention from more valuable plants, making it easier to control and manage aphid populations.
Using Insecticidal Plants – Step-by-Step Guide:
Choose the Right Plants:
- Nasturtiums: These colorful, edible flowers produce a mustard-like scent that repels aphids. Plant nasturtiums around your susceptible crops as a barrier.
- Chives and Garlic: The strong odor of chives and garlic is unappealing to aphids. Interplant them with susceptible crops or create borders using these plants.
- Marigolds: Marigolds emit a pungent scent that deters aphids and other pests. Plant marigolds throughout your garden or around vulnerable plants.
Planting and Placement:
- Companion Planting: Integrate insecticidal plants throughout your garden as companion plants. Interplant them with susceptible crops or create small clusters around them.
- Border Planting: Create a border of insecticidal plants around your garden or individual crop beds to act as a protective barrier.
- Trap Crop Planting: If using trap crops, plant them at the edges of your garden or in a separate area to attract aphids away from your main crops.
Regular Maintenance:
- Inspect for Aphids: Regularly inspect your insecticidal plants and main crops for signs of aphids. Promptly address any aphid infestations to prevent them from spreading.
- Replace as Needed: If insecticidal plants become heavily infested with aphids, replace them with new healthy plants to maintain their effectiveness.
Tips for Effective Use of Insecticidal Plants:
- Utilize a mix of different insecticidal plants to create a diverse and robust defense against aphids.
- Combine insecticidal plants with other natural control methods like attracting beneficial insects and using reflective mulch for a comprehensive approach to aphid management.
By incorporating insecticidal plants into your garden, you can create a naturally protected and aphid-resistant environment. Embrace the power of these natural defenders and enjoy the benefits of a thriving, pest-free garden without relying on chemical pesticides.

High-Quality Soil
Having high-quality soil is the foundation for creating a healthy and resilient garden that is less susceptible to aphid infestations. While soil alone may not directly get rid of or deter aphids, it plays a crucial role in promoting the overall health of plants and improving their ability to resist pests, including aphids. Here’s how high-quality soil contributes to aphid resistance and a detailed guide to achieving it:
How High-Quality Soil Supports Aphid Resistance:
- Vigorous Plant Growth: High-quality soil provides essential nutrients and a balanced pH level, promoting vigorous plant growth. Healthy and robust plants are better equipped to withstand aphid feeding and recover from minor aphid damage.
- Strong Root Systems: Healthy soil fosters strong root development, which enhances the plant’s ability to uptake nutrients and water. Strong roots enable plants to better tolerate aphid feeding stress.
- Enhanced Plant Immune System: Nutrient-rich soil supports the plant’s immune system, making them more resilient to aphid attacks and other stresses.
Guide to Achieving High-Quality Soil:
- Soil Testing: Conduct a soil test to determine the nutrient levels and pH of your garden soil. This information helps you understand the soil’s deficiencies and the necessary amendments.
- Organic Matter: Add organic matter such as compost, well-rotted manure, or leaf mold to your soil. Organic matter improves soil structure, drainage, and nutrient retention.
- Balanced Fertilization: Based on the soil test results, apply balanced organic or slow-release fertilizers to provide essential nutrients to your plants.
- Mulching: Apply organic mulch (e.g., compost, straw, wood chips) around plants to retain soil moisture, moderate soil temperature, and add nutrients as it breaks down.
- Crop Rotation: Practice crop rotation to reduce the buildup of aphid populations. Avoid planting the same crops or related plants in the same area consecutively.
- Watering: Ensure proper watering practices, providing enough water without overwatering. Consistent moisture helps plants stay healthy and better resist pests.
- Avoid Chemical Pesticides: Avoid using chemical pesticides that can harm beneficial insects and disrupt the natural balance in your garden.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect plants for aphids and promptly address any infestations. Handpicking aphids or using a strong water spray can be effective for small populations.
By focusing on high-quality soil and overall plant health, you can create a garden environment that is more resistant to aphid infestations. Embrace these natural methods and enjoy the benefits of a thriving, pest-resistant garden without relying on harmful pesticides.
Remember that a combination of these methods might yield better results, and regular monitoring and maintenance are essential for a pest-free garden. By employing these techniques, you can achieve long-term aphid control and maintain healthy, thriving plants.
Preventing Aphid Infestations
Preventing aphid infestations and maintaining a pest-resistant garden involves a combination of proactive strategies aimed at creating a balanced and healthy ecosystem. By implementing these preventive measures, you can reduce the likelihood of aphid problems and keep your garden thriving:
- Companion Planting: Utilize companion planting techniques to deter aphids and create a diverse garden ecosystem. Plant aromatic herbs like mint, chives, and garlic near susceptible plants to repel aphids.
- Attract Beneficial Insects: Encourage natural predators such as ladybugs, lacewings, hoverflies, and parasitic wasps in your garden. Plant nectar and pollen-rich flowers to attract these beneficial insects, which will help keep aphid populations in check.
- Maintain High-Quality Soil: As discussed earlier, healthy and nutrient-rich soil supports plant growth and improves plant resistance to pests, including aphids. Regularly amend the soil with organic matter and fertilizers to maintain soil health.
- Crop Rotation: Practice crop rotation to disrupt aphid life cycles and reduce the buildup of aphid populations. Avoid planting the same crops or related plants in the same area consecutively.
- Reflective Mulch: Use reflective mulch around susceptible plants to create an unappealing environment for aphids. Reflective mulch can disorient and confuse aphids, deterring them from settling on your plants.
- Insecticidal Plants: Integrate insecticidal plants like nasturtiums, chives, garlic, and marigolds as companion plants or borders to repel aphids and create a natural barrier against infestations.
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of aphids or other pests. Early detection allows for prompt intervention and prevents infestations from spreading.
- Pruning and Cleaning: Remove and dispose of any infested or damaged plant material promptly. Pruning affected plant parts can prevent aphids from spreading to healthier areas.
- Watering Practices: Practice proper watering techniques, avoiding overwatering, which can create conditions favorable to aphid proliferation.
- Natural Remedies: When dealing with small aphid populations, use natural remedies like water sprays, handpicking, neem oil, or insecticidal soap to manage the issue before it becomes widespread.
- Reduce Stress: Maintain proper plant health by providing adequate sunlight, spacing plants appropriately, and avoiding overcrowding. Stressed plants are more susceptible to aphid attacks.
- Resist Chemical Pesticides: Avoid using chemical pesticides that can harm beneficial insects and upset the natural balance in your garden. Instead, opt for organic and natural pest control methods.

Proper Plant Care and Maintenance to Prevent Infestations:
- Adequate Spacing: Properly space your plants to allow for good air circulation. Crowded plants are more susceptible to aphid infestations due to restricted airflow.
- Healthy Plants: Keep your plants healthy by providing them with sufficient sunlight, water, and nutrients. Strong and vigorous plants are more resilient to aphid attacks.
- Remove Weeds: Remove weeds around your garden, as they can act as alternative hosts for aphids and attract pests to your cultivated plants.
- Pruning: Regularly prune and remove dead or infested plant parts. Pruning can prevent aphids from spreading and improve overall plant health.
- Clean Garden Tools: Clean and disinfect your garden tools regularly to avoid inadvertently spreading aphids from one plant to another.
By combining these preventive measures, you can create a pest-resistant garden that is naturally balanced and less prone to aphid infestations. Embrace these eco-friendly practices and enjoy the benefits of a beautiful and thriving garden, free from harmful chemical interventions.
How to Get Rid of Aphids Permanently FAQs?
Can aphids harm humans or pets?
No, aphids do not pose a direct threat to pets or humans. They are specific plant pests and primarily feed on the sap of plants by piercing their stems and leaves. While aphids can cause damage to plants, they do not transmit diseases to humans or animals.
However, it’s essential to wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly before consumption to remove any aphids or their honeydew residue, which can attract other pests.
How quickly do aphids reproduce?
Aphids are known for their rapid reproduction rate. Under ideal conditions, aphids can go from birth to maturity in as little as one week.
Females can give birth to live nymphs without mating, and each adult aphid can produce numerous offspring throughout their lifespan. As a result, aphid populations can explode quickly, leading to infestations if left unchecked.
What time of year are aphids most active?
Aphids are active during the warmer months of the year, typically from spring through fall. Their activity peaks in the late spring and early summer when temperatures are favorable for their reproduction and feeding.
During the colder months of winter, aphid activity decreases, and many aphid species may overwinter as eggs on plants or in the soil.
Are chemical pesticides safe for the environment?
The safety of chemical pesticides for the environment depends on the specific pesticides used and how they are applied. Some chemical pesticides can have harmful effects on beneficial insects, pollinators, birds, and other non-target organisms.
They may also contaminate soil and water, leading to unintended environmental consequences. To minimize environmental impact, it is advisable to use chemical pesticides as a last resort and opt for more eco-friendly alternatives, such as natural predators, reflective mulch, insecticidal plants, and biological controls like beneficial nematodes.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) practices can help strike a balance between pest control and environmental protection by combining various methods to manage aphids and other garden pests sustainably.
Always read and follow the instructions on pesticide labels carefully and consider the potential risks and benefits before using chemical pesticides. In many cases, non-chemical methods can be just as effective in controlling aphids while promoting a healthy and balanced garden ecosystem.
Can aphids develop resistance to control methods?
Yes, aphids can develop resistance to certain control methods over time. This is a common phenomenon observed in many pest species when exposed repeatedly to the same control measures, such as chemical pesticides.
Aphids with genetic traits that provide some resistance to the control method may survive and pass on these traits to their offspring. Consequently, the population becomes less susceptible to that particular control method.
To manage and prevent resistance, it is crucial to implement Integrated Pest Management (IPM) practices. IPM involves using a combination of different control methods, rotating control options, and regularly monitoring pest populations. By diversifying control measures, aphids are less likely to develop resistance, and the overall effectiveness of pest management is improved.

Is it possible to have a completely aphid-free garden?
Achieving a completely aphid-free garden is challenging, as aphids are widespread and can be carried by wind, insects, and animals. Moreover, aphids reproduce rapidly, making it difficult to eliminate every single individual.
However, with effective preventive measures and proactive pest management strategies, it is possible to maintain aphid populations at manageable levels and minimize damage to plants.
Creating a healthy garden environment that promotes biodiversity, attracts beneficial insects, and implements natural pest control methods can significantly reduce aphid infestations. A combination of techniques, including reflective mulch, insecticidal plants, beneficial nematodes, and encouraging natural predators, can help keep aphid populations under control and maintain a thriving, pest-resistant garden.
Can I use neem oil indoors for houseplants?
Yes, neem oil can be used indoors for houseplants as a natural and safe pest control option. Neem oil is derived from the neem tree and contains compounds that act as insecticides and repellents against various pests, including aphids. When using neem oil indoors, it is essential to follow these guidelines:
- Dilute Properly: Mix neem oil according to the instructions on the product label. Usually, one teaspoon of neem oil per quart of water is sufficient for a spray solution.
- Test on a Small Area: Before applying neem oil to the entire houseplant, test it on a small, inconspicuous part of the plant to ensure it does not cause any adverse reactions.
- Even Application: Apply the neem oil spray evenly on all parts of the plant, including the undersides of leaves where aphids often hide.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Apply neem oil in the early morning or late afternoon to avoid direct sunlight, as this can cause leaf burn.
- Repeat as Needed: Neem oil may need to be reapplied every one to two weeks or after heavy rain to maintain its effectiveness.
How long does it take for insecticidal soap to work?
Insecticidal soap works by disrupting the cell membranes of insects, including aphids, causing dehydration and death. The effectiveness and speed of action depend on various factors, such as the concentration of the soap, the target insect species, and the application method.
Generally, insecticidal soap can start to show results within minutes to hours after application. Aphids that come into direct contact with the soap solution will begin to show signs of stress and eventual death. However, insecticidal soap may not be as effective against aphids with waxy or protective coatings.
For best results, ensure thorough coverage of the aphids and repeat applications as needed to target newly hatched nymphs or any survivors from the initial treatment. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions on the product label for the correct dilution and application guidelines.
Conclusion
Effectively managing and preventing aphid infestations in your garden requires a combination of proactive strategies and eco-friendly control methods. By promoting a healthy garden ecosystem through high-quality soil, companion planting, and attracting beneficial insects, you can naturally get rid of aphids permanently, deter, and reduce their impact on your plants.
Implementing good gardening practices, like regular inspections and proper plant care, enables early detection and prompt intervention when aphid populations are low.
Avoiding chemical pesticides and opting for natural alternatives, such as neem oil, insecticidal soap, and reflective mulch, maintains a balanced environment while keeping aphid numbers in check.
While achieving a completely aphid-free garden may be challenging, diligent application of preventive measures and integrated pest management fosters a thriving and pest-resistant garden.
Embrace these methods to enjoy the beauty and productivity of your garden while coexisting harmoniously with nature. With vigilance, care, and ecological consciousness, your garden can flourish, free from the harmful effects of aphid infestations.
